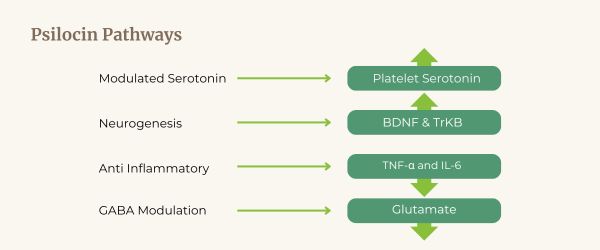
Psilocin is a serotonin agonist, modulation of serotonin receptors influences mood, cognition, and motor symptoms associated with the disease. It has been shown to enhance neuroplasticity and promote neurogenesis in preclinical studies, by stimulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and its receptor TrkB, psilocin should promote neuronal survival and plasticity. Psilocin’s activity at N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptors could potentially modulate glutamate neurotransmission, influencing excitotoxicity and neuronal death observed in neurodegenerative processes. Psilocin is known to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which should neuroinflammation. Psilocin has been shown to modulate mitochondrial function, this potential should improve mitochondrial health and function in neurons.